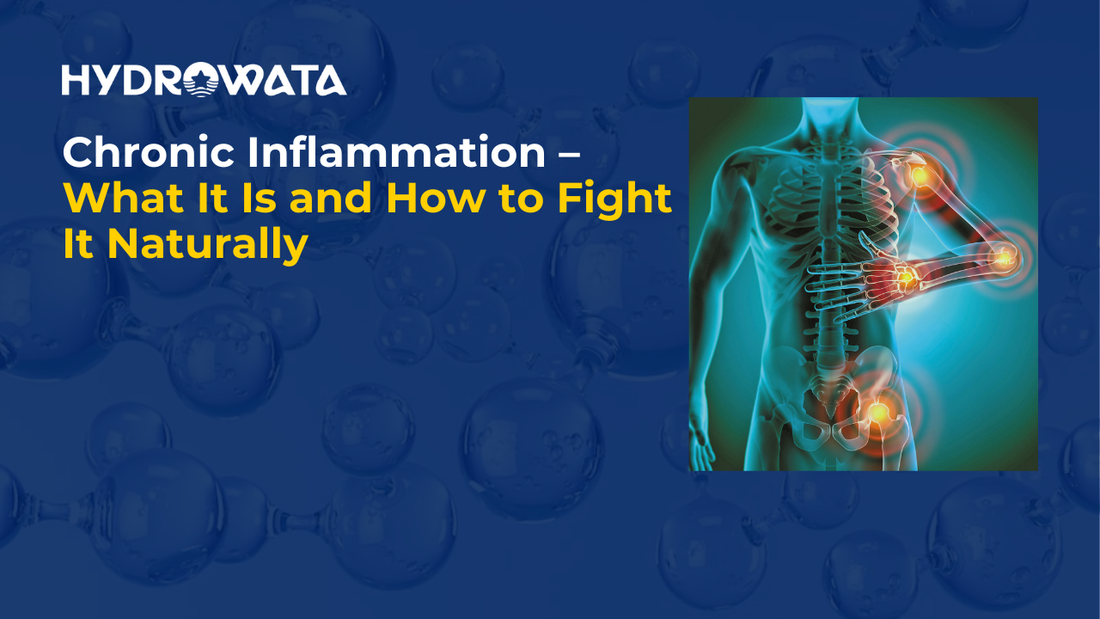
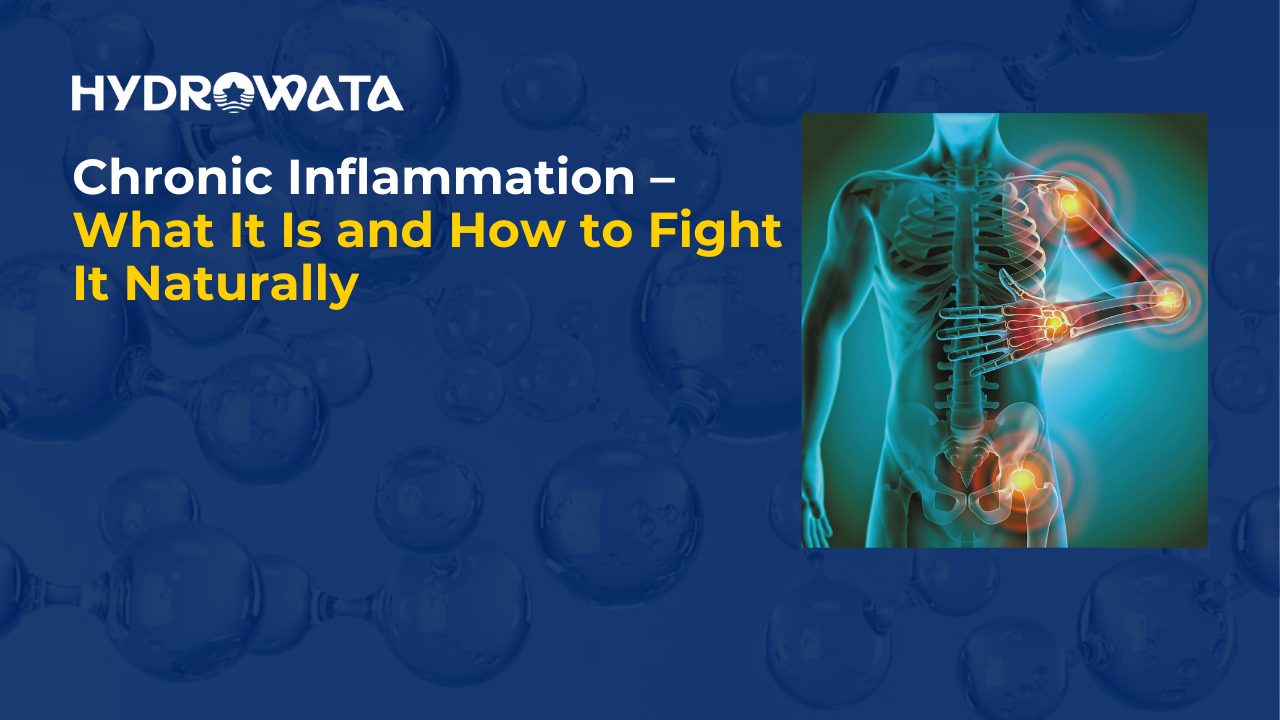
Chronic inflammation is an invisible force that quietly undermines your health over time. Unlike acute inflammation, which helps heal injuries, chronic inflammation lingers in the body and can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions.
The good news? Natural strategies like proper hydration, nutrition, and stress management can help fight back. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, signs, and ways to reduce chronic inflammation—and introduce HydroWata, a powerful hydrogen water bottle designed to support your wellness journey every day.
What is Chronic Inflammation

Chronic inflammation is your body’s prolonged immune response to harmful stimuli—like toxins, infections, or unhealthy habits. While short-term (acute) inflammation is a healthy, protective process, chronic inflammation persists for weeks, months, or even years, gradually damaging tissues and organs.
It can silently contribute to numerous conditions, including arthritis, heart disease, cancer, and neurological issues. Often, it operates beneath the surface, with mild but nagging symptoms.
Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, stress, lack of exercise, and dehydration can all trigger or worsen it. Understanding what drives this type of inflammation is the first step toward restoring long-term health.
Common Causes of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged and persistent immune response that can last for months or even years. Unlike acute inflammation, which helps the body heal from injury or infection, chronic inflammation can damage healthy tissues and contribute to various diseases. Understanding the common causes of chronic inflammation is key to managing and preventing its harmful effects.
Poor Diet
One of the biggest culprits behind chronic inflammation is the modern diet. Highly processed foods, added sugars, trans fats, and excessive red meat can all contribute. These foods create an imbalance in the gut microbiome and trigger inflammatory responses. Diets low in fiber and antioxidants leave the body defenseless against oxidative stress, compounding inflammation.
Obesity
Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, leads to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These molecules promote chronic inflammation throughout the body, putting you at higher risk of insulin resistance, cardiovascular issues, and metabolic syndrome.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity reduces the body’s ability to fight inflammation. Regular exercise boosts circulation, supports the immune system, and lowers inflammatory markers. A sedentary lifestyle not only increases weight gain but also suppresses the body’s natural anti-inflammatory processes.
Chronic Stress
When the body remains in a constant state of stress, it continuously produces cortisol and other stress hormones. Over time, this leads to imbalances in the immune system and persistent low-level inflammation.
Environmental Toxins
Exposure to pollution, pesticides, heavy metals, and synthetic chemicals in everyday products can burden the body’s detox systems. These toxins often accumulate and spark ongoing immune responses.
Poor Sleep
Quality sleep is vital for repair and recovery. Sleep deprivation alters hormone levels and suppresses immune function, which can heighten inflammation and increase vulnerability to illness.
Smoking and Alcohol Use
Both habits introduce harmful chemicals into the body and impair its ability to manage inflammation. Smoking damages tissue and blood vessels, while alcohol overuse burdens the liver and contributes to systemic inflammation.
Dehydration
Water helps flush toxins, support digestion, and maintain healthy cellular functions. Without enough water, the body becomes more acidic, and waste accumulates, both of which can increase inflammation.
Understanding these root causes helps guide effective changes in diet, lifestyle, and self-care habits. When addressed, the body can begin to heal, and inflammation levels can drop significantly, promoting better health and energy.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For

Chronic inflammation often develops silently over time, and its symptoms can be subtle or easily mistaken for other health issues. However, recognizing these warning signs early can be crucial in preventing more serious health complications. The body frequently gives signals that something is amiss, and paying attention to these can help you seek timely medical advice and interventions.
Fatigue
One of the most common and frustrating symptoms of chronic inflammation is persistent fatigue. Unlike normal tiredness, this kind of exhaustion doesn’t improve significantly with rest or sleep.
This happens because inflammation can impair mitochondrial function—the energy-producing structures within your cells—resulting in a decreased capacity to generate energy. This chronic low energy can affect your productivity, mood, and overall quality of life.
Joint and Muscle Pain
Ongoing aches, stiffness, or swelling in the joints and muscles can be a key indicator of chronic inflammation. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and fibromyalgia are linked to prolonged inflammatory processes attacking healthy tissue. The pain may worsen with activity or in the morning and can gradually limit mobility and physical function.
Digestive Issues
The gut is especially vulnerable to the effects of inflammation. Persistent digestive symptoms like bloating, cramping, excessive gas, constipation, or diarrhea may signal underlying inflammatory conditions such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
These symptoms arise because inflammation disrupts the delicate balance of the gut lining and microbiome, leading to impaired digestion and nutrient absorption.
Brain Fog
Cognitive symptoms like difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, or mental sluggishness are increasingly recognized as effects of chronic inflammation on the brain and nervous system. Inflammation can affect neurotransmitter function and brain signaling, leading to decreased mental clarity, slower processing speeds, and mood changes.
Skin Problems
The skin often acts as a visible reflection of internal health. Chronic inflammation may manifest as eczema, psoriasis, acne, or persistent unexplained rashes. These conditions occur when the immune system is in a constant state of activation, causing skin cells to become inflamed and irritated.
Frequent Infections
If you find yourself catching colds, flu, or other infections more often than usual, chronic inflammation might be interfering with your immune system’s ability to respond properly. Inflammation can dysregulate immune function, leaving you more vulnerable to pathogens and prolonging recovery times.
Weight Gain or Difficulty Losing Weight
Inflammation can influence hormones involved in metabolism and appetite regulation, such as insulin and leptin. This hormonal disruption often leads to insulin resistance, making it difficult to lose weight and easier to gain fat, particularly around the abdomen. Chronic inflammation is also linked to obesity-related health issues.
Mood Swings or Depression
Increasing research highlights a strong connection between chronic inflammation and mental health conditions, including anxiety and depression. Inflammatory molecules can affect brain chemistry, influencing mood and emotional regulation. Symptoms may include irritability, sadness, loss of interest in activities, and fluctuations in energy.
Allergies or Autoimmune Reactions
In some cases, chronic inflammation results from an overactive immune system that mistakenly attacks healthy tissues or overreacts to harmless substances. This can lead to allergic reactions such as hay fever or food sensitivities, as well as autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Persistent Low-Grade Fever or Swollen Lymph Nodes
These physical signs indicate ongoing immune system activity. A low-grade fever that doesn’t resolve and swollen lymph nodes may point to continuous inflammation somewhere in the body, warranting further medical evaluation.
Recognizing these signs and symptoms early is vital. Chronic inflammation is often a hidden driver behind many chronic illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. By being aware of these indicators, you can take proactive steps—through lifestyle changes, medical treatment, or both—to reduce inflammation and protect your long-term health.
If you notice several of these symptoms persisting over weeks or months, consulting a healthcare professional is highly recommended for proper diagnosis and management.
How Inflammation Affects the Body

Inflammation is a natural defense mechanism of the body, designed to protect against injury and infection. However, when it becomes chronic, it can cause a wide array of health issues across various systems of the body. According to health experts, "inflammation is at the root of practically all known chronic health conditions."
Brain
In the brain, chronic inflammation is driven by pro-inflammatory cytokines that trigger autoimmune reactions. These reactions have been linked to mental health issues such as depression and poor memory. Furthermore, inflammation contributes to neurological disorders including Alzheimer’s disease, autism, and multiple sclerosis (MS).
Cardiovascular System
Inflammation in the heart and arteries contributes to major cardiovascular problems. It increases the risk of heart disease, strokes, and high blood sugar, a condition associated with diabetes. Inflammatory damage to blood vessels can also result in anemia.
Muscle and Bones
Inflammatory cytokines impact muscle health by causing pain and weakness. This can lead to conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome or polymyalgia rheumatica. In bones, inflammation hinders the body's ability to repair bone tissue, increasing the risk of fractures and leading to conditions like osteoporosis.
Skin
Chronic inflammation also affects the skin. It can compromise the health of the liver and kidneys, resulting in skin issues like rashes, eczema, psoriasis, and even premature aging such as wrinkles and fine lines.
Thyroid
Autoimmunity caused by inflammation can impair the thyroid gland. This disrupts thyroid hormone production and lowers thyroid receptor count, affecting metabolism and energy regulation.
Lungs
In the respiratory system, inflammation can initiate autoimmune reactions against the airway linings. This may cause or exacerbate conditions such as asthma and allergies.
Gastrointestinal Tract
The GI tract is particularly vulnerable to inflammation. Chronic inflammation damages the intestinal lining, leading to disorders like GERD, Crohn’s disease, and Celiac disease.
Kidneys
In the kidneys, inflammatory cytokines restrict blood flow, leading to complications such as edema, hypertension, nephritis, and potentially kidney failure.
Liver
Inflammation can cause the liver to enlarge or develop fatty liver disease. This results in an accumulation of toxic substances in the body and overall impaired liver function.
Natural Ways to Reduce Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation can quietly undermine your health over time, but there are effective natural strategies to help reduce it. By making mindful choices in your diet, lifestyle, and environment, you can support your body’s ability to calm inflammation and promote overall well-being. Here are seven practical ways to get started.
Adopt an Anti-Inflammatory Diet

What you eat plays a crucial role in controlling inflammation. Focus on whole, minimally processed, plant-based foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber that help fight inflammation at the cellular level. Leafy greens like spinach and kale, colorful berries, fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel, nuts, seeds, and spices like turmeric and ginger are excellent choices.
These foods contain compounds that reduce inflammatory markers and support overall immune health. At the same time, avoid or limit processed foods, refined sugars, trans fats, and artificial additives, which can trigger or worsen inflammation.
Stay Physically Active

Regular exercise is a powerful way to reduce chronic inflammation. Activities like walking, swimming, yoga, or cycling promote better circulation, help regulate hormone levels, and reduce excess body fat—all of which contribute to lowering inflammatory responses.
Exercise also encourages the release of anti-inflammatory molecules and improves immune system function. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week, combined with strength training to maximize benefits.
Manage Stress Effectively

Chronic stress is one of the leading causes of inflammation, as it triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which in excess can promote inflammatory processes. Incorporate stress-management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, mindfulness, or journaling into your daily routine.
Even simple habits like spending time in nature, listening to calming music, or engaging in hobbies can help soothe your nervous system and reduce inflammation.
Prioritize Quality Sleep

Sleep is essential for the body’s natural repair processes, including controlling inflammation. Aim to get 7 to 9 hours of restful, uninterrupted sleep each night.
Create a bedtime routine that promotes relaxation—limit exposure to screens and blue light before bed, avoid caffeine and heavy meals late in the day, and consider calming practices like reading or gentle stretching.
Poor sleep quality or insufficient sleep has been linked to higher levels of inflammatory markers, so investing in good sleep hygiene is vital.
Stay Well Hydrated

Water is essential for flushing out toxins and supporting all bodily functions, including those involved in the inflammatory response. Dehydration can exacerbate inflammation by impairing circulation and detoxification pathways.
Aim to drink plenty of clean, filtered water throughout the day. Some people find that hydrogen-rich water offers additional antioxidant benefits, although more research is needed in this area.
Limit Exposure to Environmental Toxins

Everyday exposure to chemicals found in household cleaners, personal care products, and polluted air or water can increase your toxic load and trigger inflammation. Choose natural, non-toxic cleaning agents and beauty products whenever possible.
Eating organic foods can reduce pesticide intake, and using air and water filters at home helps minimize pollutants. Creating a cleaner, toxin-free environment supports your body’s ability to maintain balanced immune function and reduce chronic inflammation.
Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption

Both smoking and excessive alcohol intake are well-known contributors to chronic inflammation and numerous health problems. Smoking introduces harmful chemicals that directly damage tissues and stimulate inflammatory responses.
Alcohol, especially when consumed in excess, disrupts gut health and immune balance. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can significantly lower inflammation levels and improve overall health outcomes.
The Role of Molecular Hydrogen in Combating Inflammation

Molecular hydrogen (H₂) is gaining scientific recognition for its ability to reduce oxidative stress, a key contributor to chronic inflammation. Unlike other antioxidants, hydrogen is selective—it targets only harmful free radicals without disrupting essential bodily functions. When consumed in water, molecular hydrogen can reach cells quickly and support cellular health.
Studies suggest that hydrogen water may lower markers of inflammation, reduce pain, and support recovery in people with inflammatory conditions. It may also help balance the immune response, reduce fatigue, and promote overall wellness. Because it is natural and safe, molecular hydrogen is an exciting tool for those looking to fight inflammation without side effects.
Why Choose HydroWata for Daily Inflammation Support

HydroWata Hydrogen Water Bottle is more than just a water bottle—it's a powerful health companion. Designed to generate high-quality hydrogen-rich water in minutes, HydroWata helps your body fight inflammation at the cellular level. Unlike other products, HydroWata is portable, rechargeable, and easy to use anywhere—at home, the gym, or on the go.
What makes HydroWata unique is its advanced technology that ensures maximum hydrogen concentration and water purity. With a sleek design and user-friendly features, it fits seamlessly into your wellness routine.
Daily use of hydrogen-rich water from HydroWata may help:
- Reduce oxidative stress
- Support joint and muscle recovery
- Improve energy and mental clarity
- Promote better digestion and skin health
It’s a safe, non-invasive addition to your wellness toolbox. There’s no need for pills or synthetic treatments—just add water, activate, and sip. Thousands of users are already experiencing the benefits of hydrogen water in their fight against inflammation.
When you choose HydroWata, you’re investing in clean hydration, backed by science and designed for real-life use. Whether you're managing symptoms or simply supporting long-term health, HydroWata is a natural way to feel your best, every day.
How to Use HydroWata for Best Results
Using HydroWata is simple and effective. Start by filling the bottle with clean, filtered water. Press the activation button, and in just a few minutes, your water is enriched with molecular hydrogen.
For best results:
- Drink 3-5 bottles per day, ideally on an empty stomach or before meals
- Use freshly generated water for maximum hydrogen concentration
- Store the bottle properly and keep it charged for consistent use
Consistency is key. Make HydroWata part of your daily wellness routine to support hydration, antioxidant intake, and inflammation reduction. Combine with a healthy lifestyle for even better results.
Conclusion: A Healthier Path Starts with a Sip
Chronic inflammation can quietly undermine your health, but you have the power to take control. Small, consistent changes like better nutrition, stress management, and clean hydration can lead to big improvements over time.
HydroWata hydrogen water bottle offers a modern solution rooted in science, providing antioxidant-rich hydration to support your body from the inside out. By incorporating hydrogen water into your daily life, you make a proactive choice toward better energy, reduced inflammation, and long-term wellness. Ready to take the next step? Make every sip count—with HydroWata.
FAQs
1. What is hydrogen water?
Hydrogen water is regular water infused with extra molecular hydrogen (H₂) gas. It contains dissolved hydrogen molecules, which act as antioxidants that may help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body.
2. Can hydrogen water help with inflammation?
Some studies suggest that hydrogen water may have anti-inflammatory properties by reducing oxidative stress and lowering inflammatory markers. While research is promising, more large-scale human studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness.
3. Is HydroWata safe to use daily?
Yes, HydroWata is generally considered safe for daily use as it is simply water enriched with molecular hydrogen. However, always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and consult your healthcare provider if you have specific health concerns.
4. How quickly will I feel the effects?
The effects of hydrogen water can vary depending on the individual and the condition being addressed. Some people report feeling increased energy or reduced inflammation within days, while for others it may take weeks of consistent use.
5. Are there any side effects?
Hydrogen water is usually well tolerated with no known significant side effects. However, if you have underlying health conditions or are pregnant, it’s best to consult your doctor before adding hydrogen water to your routine.